Service Container
Containers are a standardized and portable way to package software applications and their dependencies, allowing for consistent performance across different computing environments.
Service Containers are recommended for long-running services and applications that require a high level of stability. They offer a high level of control over the underlying infrastructure, making it a suitable choice for APIs, Web Applications, or long running Workers.
This guide covers how you can deploy a Service Container to your Kubernetes cluster using Zeet.
1. Select Service Container Project Type
To get started, head over to the Zeet dashboard and navigate to the Create New menu. Here, select the Service Container Project Type.
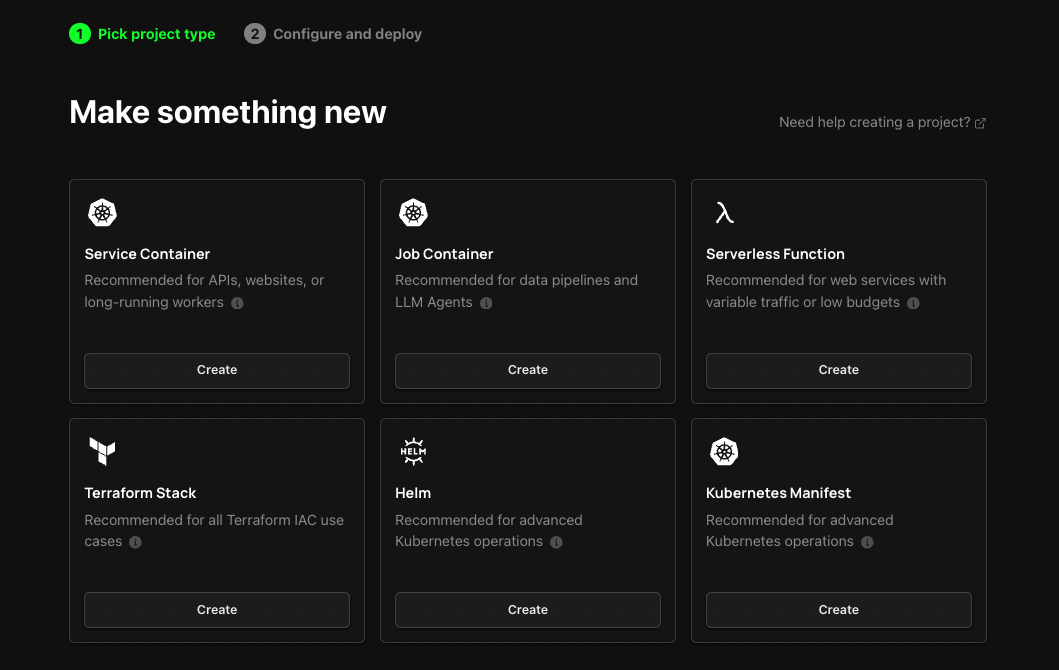
2. Configure Project
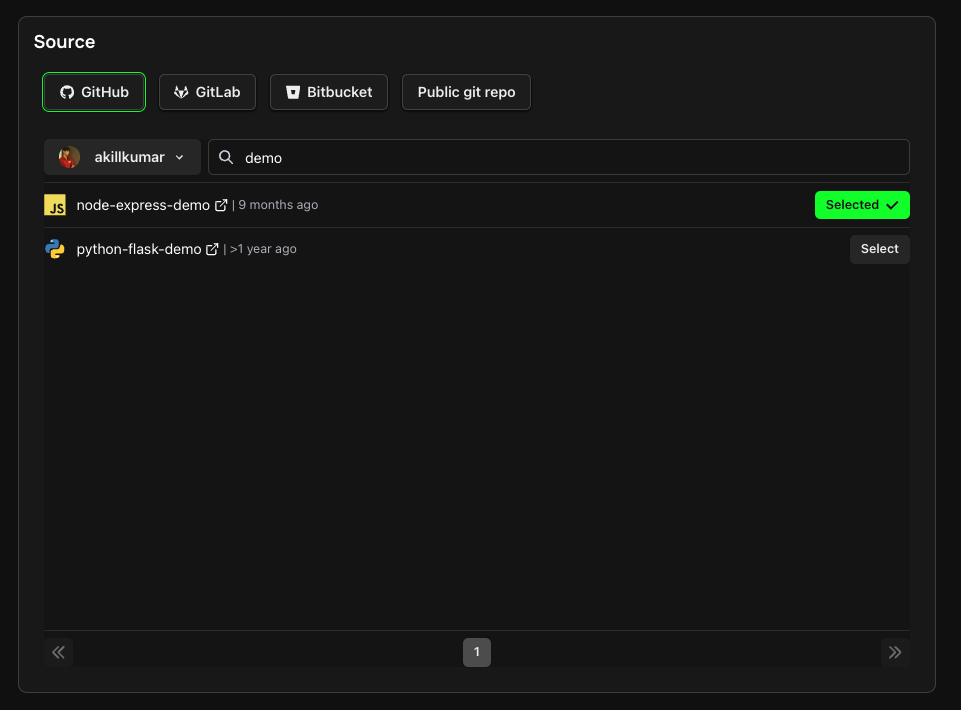
1. Pick your Source
The first step in configuring your deployment is to select your Project source. Select a repository from your connected GitHub/ GitLab/ BitBucket account, deploy directly from any public git repository, or from a connected Docker registry.
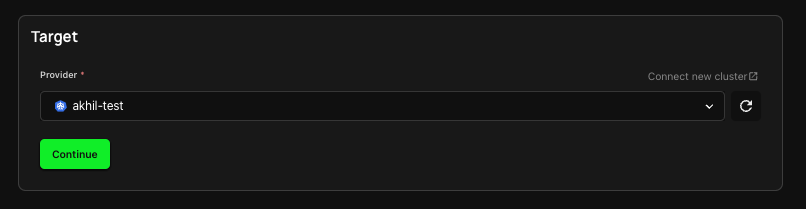
2. Select Target
The next step is selecting your Deploy target. For a Service Container, this would mean selecting your Cluster. If you don't already have a Cluster connected, follow the link here to create or link a new Cluster.
3. Configure Inputs
You've got the source and target covered, now it's time to configure the inputs for your Project.
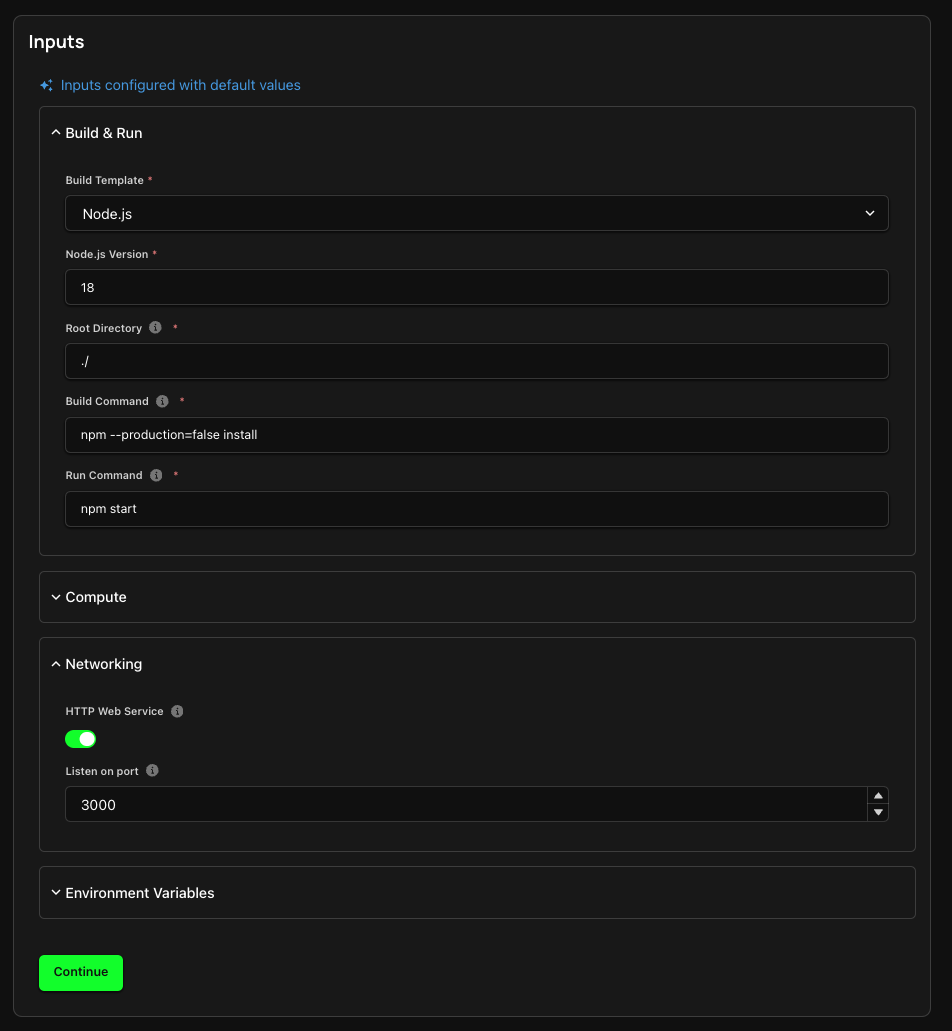
- Here, you can configure your Build & Run settings, including your Build Type, Build and Run commands, and your working directory.
- The Compute section allows you to configure the CPU/ Memory you require for your container. You can also elect to use spot instances here.
- Under the Networking tab, you can expose the port that your Service Container listens on.
- You can also add any Environment variables that your app would require during build-time and run-time.
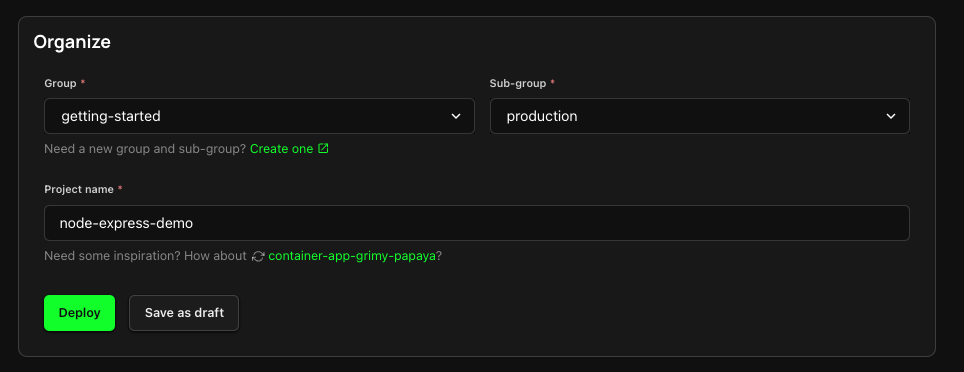
4. Finalize and Deploy!
You're almost there! Give your new Project a name and organize it within a Group and Sub-Group. You can deploy your Project right away, or choose to save it as a draft to deploy later.